How Does a Home Heating System Work?
What Parts Go Into a Heating System?
Every home heat system is made up of three key parts:
- Heat Source. A heat source is the first step of every home heating process. It’s a thermal power generator that uses energy materials and alternates them into heat. The heat source is generally placed in the basement or your back garden. The most common types use a heat pump, furnace, or boiler, but there are also some less common alternatives like solar panels.
- Distribution System. A complex system of ducts or pipes that spread the heat all over your house.
- Control System. Typically, a thermostat controls the temperature at which the heat pump operates. They’re centrally operated units with a display or buttons regulating the degrees and the cooling/heating switch of your system.
Types of Heating Systems
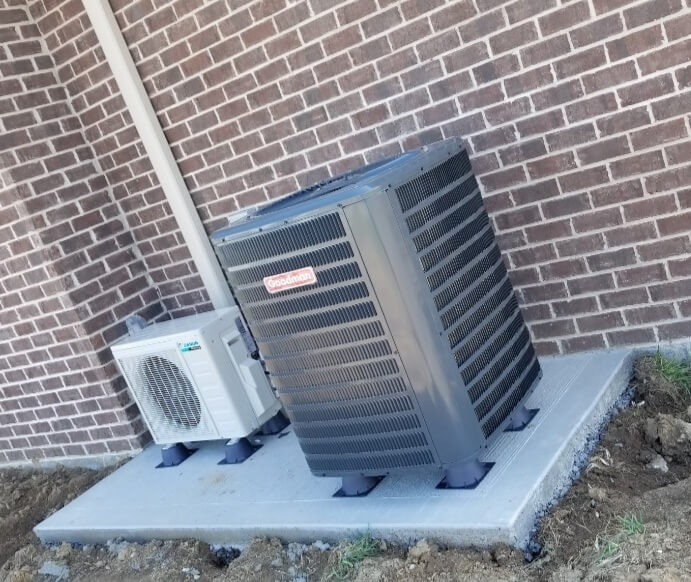
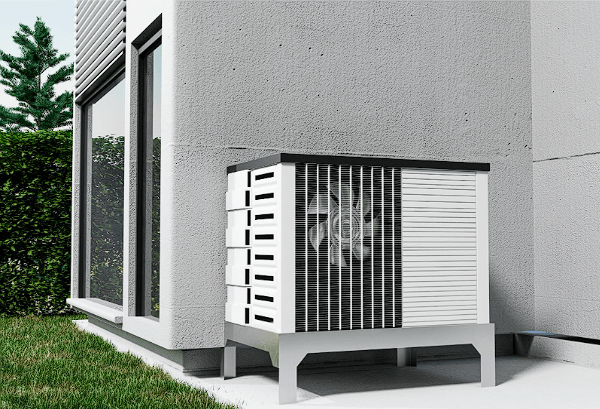
Heat Pump
Some of the main advantages of using a heat pump system are:
- Energy Efficiency. Air-to-air heat pumps use almost half the electricity of other electrical heaters like furnaces. Geothermal ones are even more efficient in warming up your space with very little energy used, if applicable to your living situation.
- Versatility. The ductwork of a heat pump system can be used to keep your house warm during winter and cool during summer. It makes them much more versatile than radiator units, which can only provide heat.
- Environmentally Friendly. These produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to combustion-based heating systems, making them a greener option.
- Installment Costs. Purchasing and installing a heat pump system might be more expensive than some traditional heat systems.
- High Maintenance. Due to having tricky parts like filters and coils, heat pumps require a lot more maintenance over the year.
- Inefficiency in Extreme Cold. Heat pumps won’t be as effective as fuel-based heating systems in extremely low temperatures. They need at least a moderately cold climate to extract warm air from the outside.
- Moderate Climates. Due to their inefficiency in extreme colds, heat pump systems are best for houses in areas of moderate climate.
- All-electric Homes. New homes that run every appliance on electricity will be great as you won’t need to install new gas pipes or coal boilers.
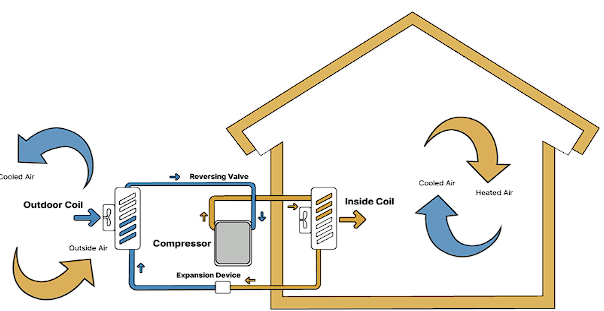
Furnace
- Quick Heating. Contrary to heat pumps, furnaces don’t rely on outdoor thermal sources. They burn store-bought fuel and heat your home much faster.
- Cheap to Run. Gas is relatively affordable, making furnaces very cost-effective and cheap to maintain.
- Even Warmth. Furnaces use ducted tubes to spread warmth, meaning all your rooms will be evenly heated.
- Carbon Footprint. According to a Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) study, furnaces have up to 50% higher carbon footprint compared to heat pumps. Combustion-based heaters emit greenhouse gases, massively contributing to environmental concerns.
- Take up a Lot of Space. Having a large basement means a lot of storage, but still, furnaces can take up a lot of space in your home. Especially if you have to install ductwork all over the house.
- Cold Climates. Places where winter temperatures often go way below the freezing point will be ideal for furnace heating. Their fast and independent heater will warm up your house quickly, even if you leave it turned off for days.
- Houses with Installed Ducts. Having pre-installed ducts is a huge upside when considering any heating system that operates on circulating air. It can cut installation costs by thousands of dollars.
- Houses with Cheap Gas Access. Gas prices have been significantly surging over the past few years. If you live in areas like the West Coast, where prices are quite inflated, you might want to reconsider other options.
Boiler
Radiating heating systems are not that popular in the US. The latest research shows that as of last year, only 8 thousand new houses were built using these systems. Their inability to cool down the house in summer badly damaged the reputation of boilers.
Although a less common option, there are many reasons to choose a boiler over a heat pump or furnace:
- Cost-effective. Water takes less energy to heat than air and stays warmer for longer. This makes boilers cheaper to run as they take less fuel to heat your house at the same temperature for the same duration.
- Better Indoor Air Quality. Radiator heating doesn’t remove moisture from your room as forced air venting does. It is thus more humid and comfortable, unlike furnaces, which blow the air over an open flame.
- Floor Heating. Only people who have walked over a heated floor know the true advantage of it. Your feet are the main acceptors of cold temperatures. Using floor pipes to heat your home can feel mesmerizing during cold winters.
- High Initial Costs. Because many houses don’t have pre-installed pipes, it can cost you a lot to complete the installation. Additionally, not many HVAC experts specialize in boiler maintenance due to the fact they are so uncommon.
- No Cooling Option. The main disadvantage of boiler systems is their lack of cooling options. You’ll need to install a separate AC unit to cool down the living space in summer.
- Older Houses. Old houses with pre-installed pipes are great for boiler heating as they cover the main con of these systems – installation.
- Preference for Floor Heating. Many people have a strong preference for floor heating. If you belong to that group, boilers are the way to go.
Keeping Your Home Warm
With over 15 years of experience in the field, our main mission at Value HVAC Services is to help you make the best decision for your needs. Wherever you live and whatever the reason you’re looking for a new heating system, don’t hesitate to contact us on our website or email, or feel free to visit us in person.




